Key Exchange
Establishing trust with Participants
By default, any data stored in Smart Contracts is encrypted. This is also true for profiles, Digital Twins and other tools. As a result, it is impossible for others to read data in external contracts. Users can’t read each others contacts etc. and sending BMail to each other requires a proper key exchange to have occurred beforehand.
To establish communication, identities need to exchange keys. This is one of the most basic operations in evan.network, because without exchanging keys, little else can be done. If you are an end user, it is done for you in most cases and you won’t even notice. Otherwise, you can use the contacts ÐApp to initiate key exchanges.
How keys are exchanged
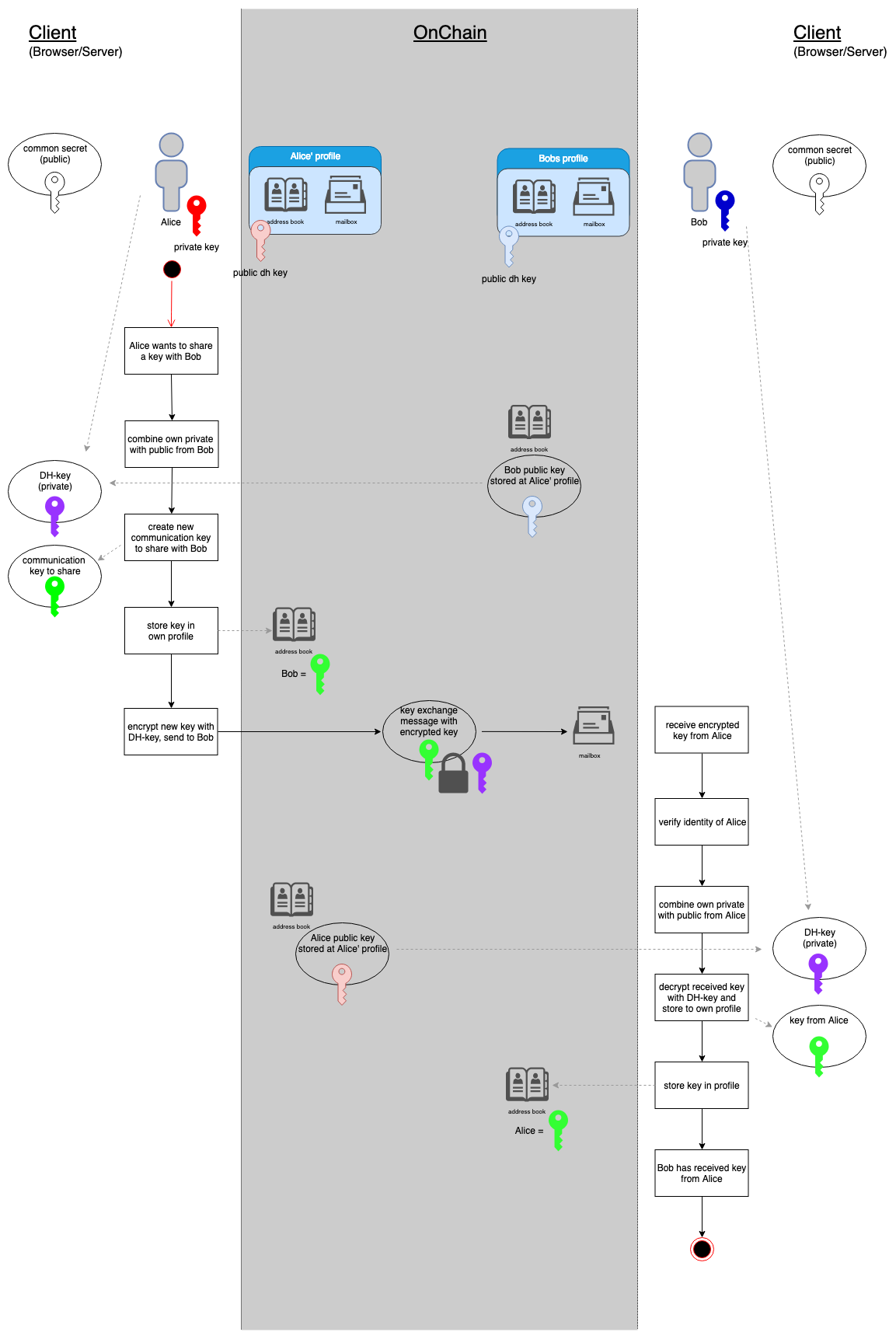
When two parties want to start communicating, they first need to exchange a communication key. This key is later on used to encrypt messages between these two and for sharing further keys (see last illustration).
Communication keys are exchanged via Diffie-Hellman key exchange, which is usually described as following:
- both parties commit on a common (publicly known)
- both parties own a private key, each only known to one of them
- both parties create a public key by combining the own private key and the common part
- public keys are exchanged between them and used to create a final key from each end
This approach is adapted and used on evan.network in this way:
- common part is publicly known and known to the API
- both parties create private and public key at identity creation
- public key is stored a the profile of each identity and can be accessed by everyone, so no extra communication is required to get another parties public key
- Diffie-Hellman key can be creating by combining own private key and public key from other parties profile (called “exchange key”)
- exchange key is used to encrypt and share the “communication key” with the other party, this is done via the mailbox
- as public key can be retrieved from profile and the encrypted communication key can be send to mailbox, this process can be initiated by one side, if a confirmation is not required, the process is completed at the initiators end
- the other party can finalize at its end at any time, optionally a confirmation can be send to the initiator
The following illustration shows the entire key exchange process:
The key exchange is available as a module in the blockchain core API library and usage examples can be found in it Basic Usage section.
Home |
FAQ |
Github Repo |
Gitter Community |
Website |
Blog |
API docu |
UI docu |
Imprint
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.