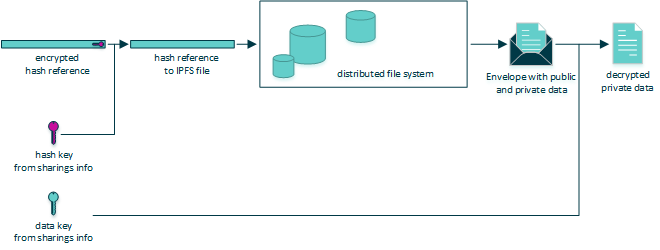
Distributed File System Encryption
Envelopes
As basically all data, which can be described as ‘content’, is stored via the hybrid storage approach, the main part of data are stored in the distributed file system. This data is encrypted and stored in so called ‘envelopes’, which are a containers for the data itself and contain enough information for the API to determine which key to use for decryption and where to retrieve the key from.
This is an example envelope:
{
"public": {
"name": "envelope example"
},
"private": "...",
"cryptoInfo": {
"algorithm": "aes-256-cbc",
"keyLength": 256,
"originator": "0xf95c14e6953c95195639e8266ab1a6850864d59a829da9f9b13602ee522f672b",
"block": 123
}
}
The ‘public’ section contains data that is visible without being invited to it or related to the contract. The ‘private’ section can only be decrypted, if the user tries to read the data has been added to the sharings of the contract. The cryptoInfo part is used to determine, which decryption algorithm to use and where to look for it.
When decrypted, the private section takes precedence over the public section. This can lead to the private section overwriting sections of the public part. For example, a public title may be replaced with a ‘true’ title (only visible for members) from the private section.
Hash Encryption
When envelopes are stored in the distributed file system, they can be retrieved via a hash. It is similar to an address of the data. This hash is then stored in the Smart Contract and contract participants can get the hash from the contract, retrieve the data from the DFS and decrypt it. To prevent data hoarders from pulling hashes from Smart Contracts, storing the DFS files for them and brute forcing them later on, hashes are encrypted before storing them in the Smart Contract as well.
Crypto Algorithms
aes-256-cbc
The default encryption is AES with cypher block chaining and a key length of 256 bit. This is commonly used for encrypting data in the API.
aes-blob
The actual encryption in this mode utilizes ‘aes’ as well, but the private part only holds a reference to the encrypted file or files in the distributed file system and the envelope is basically a listing with references to the encrypted files.
aes-ecb
This algorithm is used for encrypting file hashes, which are 32 byte values. ‘ecb’ ensures that encrypted hashes can be saved in the Smart Contract. Keys for hashes are created per contract and all hashes for a contract are encrypted with the same hash.
unencrypted
Like the name suggests, this is not an actual encryption. The envelope is just used as a wrapper for unencrypted data that follow the same guidelines. This is useful when the data scheme requires an envelope but the data should be public.
Home |
FAQ |
Github Repo |
Gitter Community |
Website |
Blog |
API docu |
UI docu |
Imprint
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.