Deployment
Deploying DApps and smart-contract means publishing the various components using a valid ENS path. These instructions assume you have used the evan.network project generator to set up your project. This project structure supports all nesecarry scripts and commands to deploy your projects.
Build and deploy smart-contracts
When your smart-contracts are comiled within the evan.network blockchain, json abi file was generated and can be used. To make these descriptions available in published ÐApps, you have to upload the ABI file and reference it within the DBCP. This can be referenced within your DBCP description files and acts as a self described contract.
ENS DApp deployment
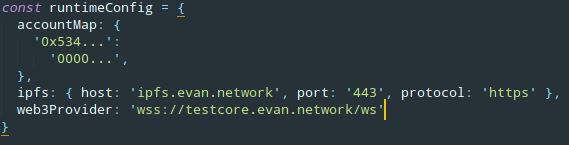
Each ÐApp can be deployed to the evan.network, so it can be accessed from anywhere, not only from a localhost server. This is handled by a wrapper library, to make the deployment as simple as possible. To deploy DApps to ens paths, you need one configuration file, that specifies which accounts and which configurations should be used for the deployment. This file must be js / json files that exports specific values deployment config.
Simply open your evan-network base project. Within your config folder, a deployment.js file is included, that contains all the important configurations for your deployment. Here you must insert your accountID and your private key, so the script can handle ENS description deployments for you.
Currently: For security reasons, the ownership of the ENS addresses are reserved for the members of the evan GmbH.
To register a ENS address, contact the evan.network team here and send us your desired ens subdomain and your accountId. (No one of the evan.network team will ask you for your data or private key! Never send your private data to others!). Mostly, the evan.network team will reserve you a sub domain, so you can manage your addresses behind, by yourself. Don’t forget to prefix the name of your DApp with the subdomain that were assigned to you (e.g. myapp.mysubdomain). When you changed the name within the dbcp.json, don’t forget to update the index.ts file of your DApp, else your application can cause an endless loop. Their you will find the following code:
return buildModuleRoutes(
`myapp.${ getDomainName() }`,
Change it to:
return buildModuleRoutes(
`myapp.mysubdomain.${ getDomainName() }`,
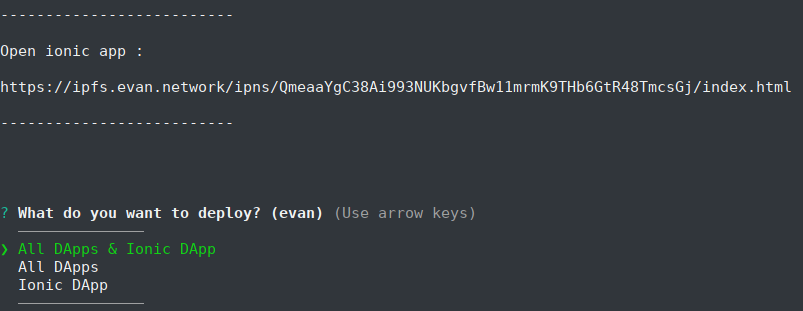
You can run the following script to choose wich projects you want to deploy.
npm run deploy pathToConfig
Be sure that “pathToConfig” is the absolute path to your deployment configuration (e.g. /path-to-my-project/config/deployment.js)!
Each ÐApp that were successfully build by “npm run dapps-build”, is available by to your deploy scope.
So, when you deploy anything, it will be available under the following ENS domain:
dappname.subdomain.evan
Now, you can open the ens address to your application on https://dashboard.test.evan.network#/my-ens-address.evan. (my-ens-address = dbcp.name) (3.3 View it in the Real World)
IPFS Deployment
If you want to deploy your application without any ENS address by using a contract, you can have a look at the standalone DApp tutorial in the section “3.1 Deploy ƉApp within an Contract”.
Home |
FAQ |
Github Repo |
Gitter Community |
Website |
Blog |
API docu |
UI docu |
Imprint
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.